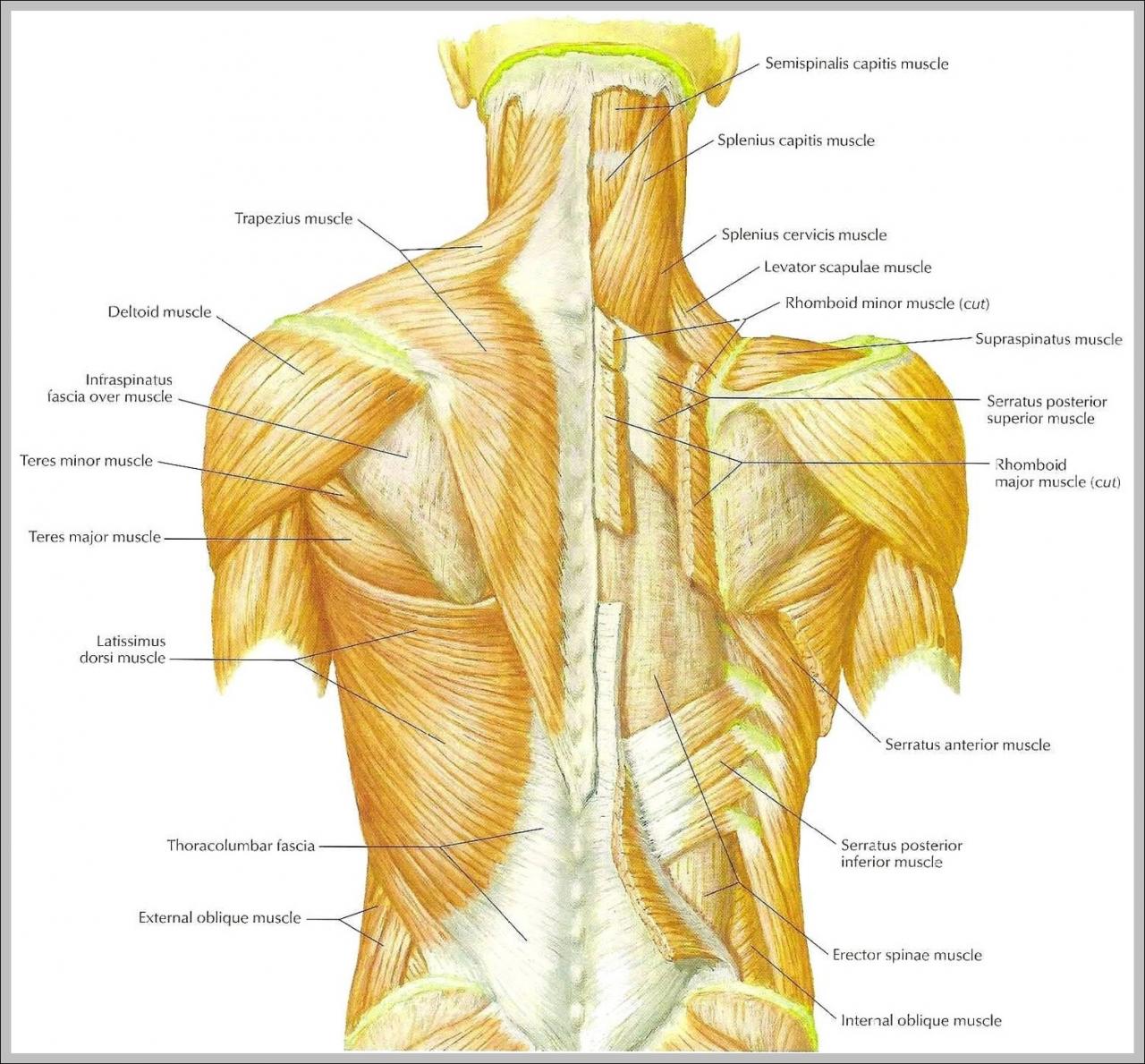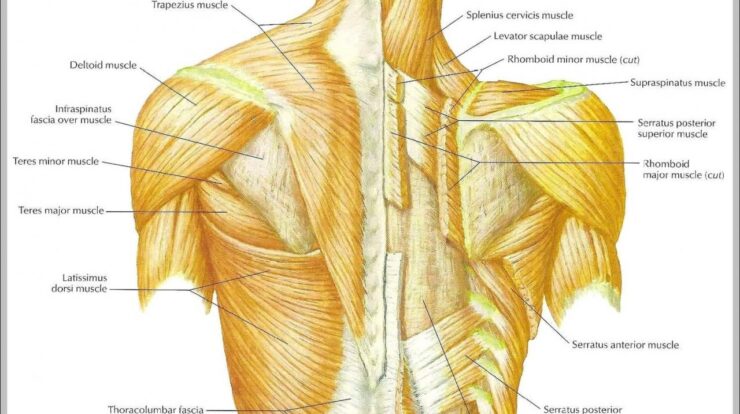
Back muscles play a crucial role in supporting our posture, movement, and overall well-being. Understanding their anatomy, functions, and common injuries can help us optimize our fitness routines and prevent muscle strains.
For those looking for inspiration, there are happy mothers day wishes for all moms images that can convey our heartfelt messages in a visual way. Additionally, happy mother’s day in vietnamese is a beautiful way to celebrate mothers in the Vietnamese community.
From exercises that target specific back muscle groups to the latest training techniques, this comprehensive guide delves into the world of back muscles, empowering you with the knowledge to strengthen and protect them.
Anatomy of Back Muscles
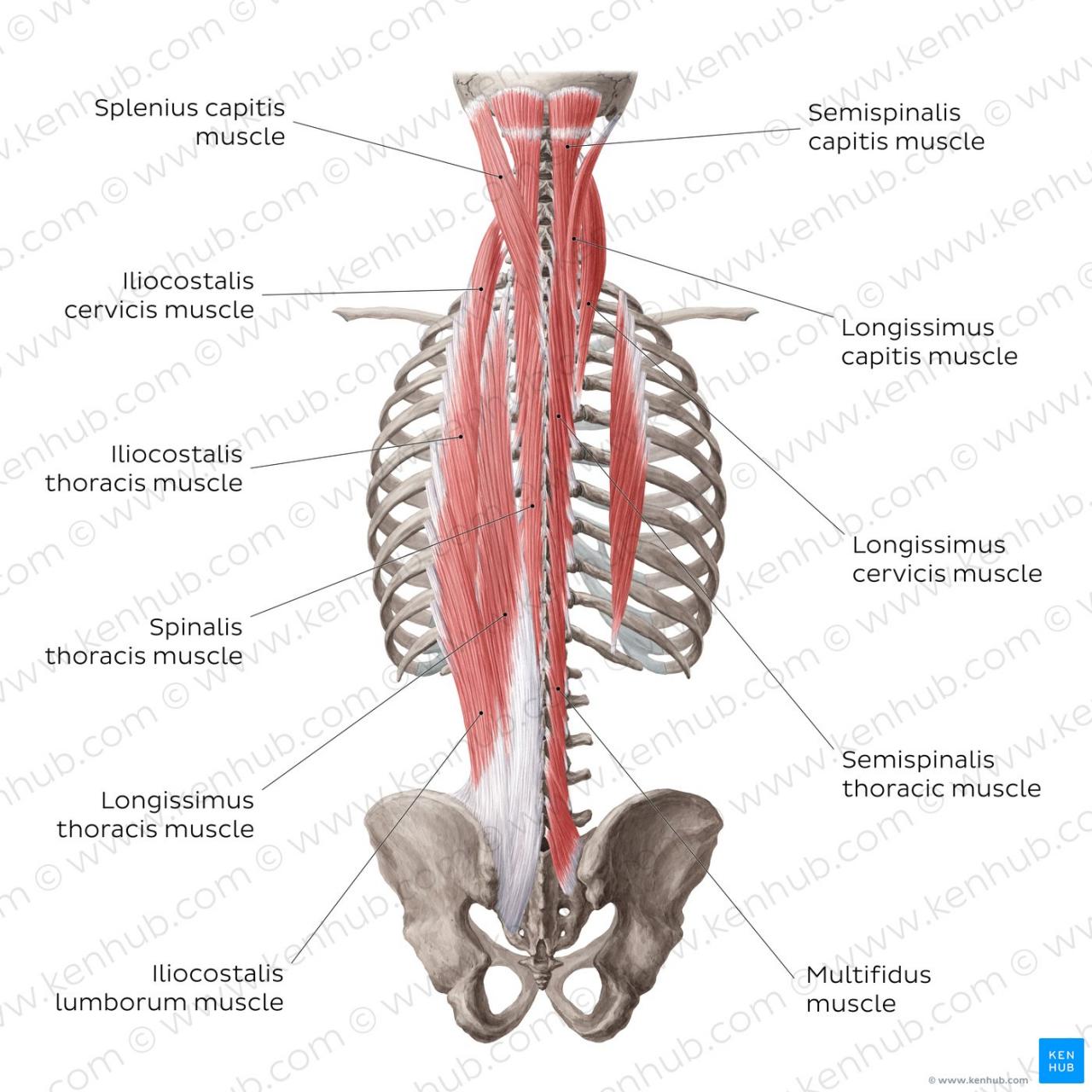
The back muscles are a complex and diverse group of muscles that play a vital role in supporting the spine, facilitating movement, and maintaining posture. Understanding their anatomy is essential for effective back training and injury prevention.
The major back muscles can be divided into two groups: superficial and deep. The superficial muscles include the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and rhomboids. The deep muscles include the erector spinae, multifidus, and rotatores.
Trapezius, Back muscles
- Origin:Occipital bone, nuchal ligament, and spinous processes of C7-T12 vertebrae
- Insertion:Clavicle, acromion, and spine of the scapula
- Function:Elevates, retracts, and rotates the scapula; extends and rotates the head
Latissimus Dorsi
- Origin:Spinous processes of T7-L5 vertebrae, lumbar fascia, iliac crest, and lower six ribs
- Insertion:Medial aspect of the humerus
- Function:Adducts, extends, and internally rotates the arm; assists in deep inspiration
Rhomboids
- Origin:Spinous processes of C7-T5 vertebrae
- Insertion:Medial border of the scapula
- Function:Retracts and elevates the scapula
Erector Spinae
- Origin:Sacrum, lumbar vertebrae, and thoracic vertebrae
- Insertion:Ribs, transverse processes of the vertebrae, and occipital bone
- Function:Extends and laterally flexes the spine; stabilizes the spine
Multifidus
- Origin:Spinous processes of the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae
- Insertion:Laminae and spinous processes of vertebrae above
- Function:Rotates and laterally flexes the spine; stabilizes the spine
Rotatores
- Origin:Transverse processes of the vertebrae
- Insertion:Laminae of vertebrae above
- Function:Rotates the spine
Final Thoughts
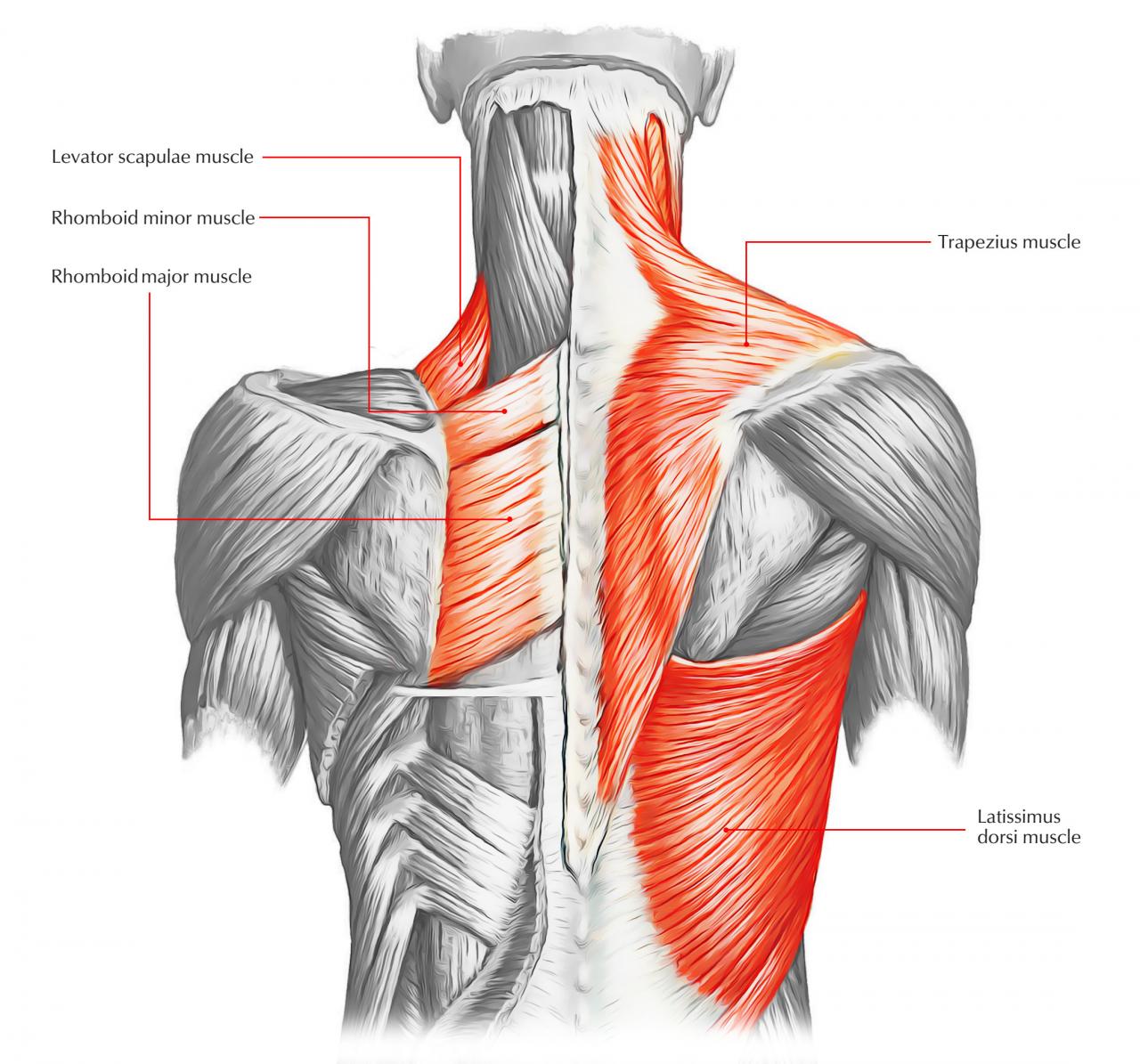
Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or simply seeking to improve your posture, understanding back muscles is essential. By incorporating targeted exercises into your routine, adopting proper form, and seeking professional advice when necessary, you can maintain strong and healthy back muscles throughout your life.
FAQ Guide
What are the major back muscle groups?
The major back muscle groups include the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, rhomboids, erector spinae, and spinalis.
As we approach Mother’s Day, let us take a moment to appreciate the special bond between mothers and their children. From heartfelt happy mothers day wishes to adorable Snoopy happy mother’s day images, there are countless ways to express our love and gratitude for the mothers in our lives.
What are the most common back muscle injuries?
Common back muscle injuries include strains, sprains, and herniated discs.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
To prevent back muscle injuries, maintain good posture, warm up before exercising, use proper lifting techniques, and strengthen your core and back muscles.